1. Glasgow coma scale (GCS)
| GCS | Response | |
| Eye | Open Spontaneously | 4 |
| Open to Verbal Command | 3 | |
| Open to Pain Stimulus | 2 | |
| No Response | 1 | |
| Verbal | Talk Spontaneously | 5 |
| Confused, Disoriented Speech | 4 | |
| Inappropriated words | 3 | |
| Incomprehensive words | 2 | |
| None | 1 | |
| Motor | Obeys | 6 |
| Localizes to Pain | 5 | |
| Withdraws from Pain | 4 | |
| Abnormal flexion, decorticate posture | 3 | |
| Extensor response, decerebrate posture | 2 | |
| None | 1 | |
| Total | 3 to 15 | ??? |
2. White and Grey Matter
| Outside | Inside | |
| Brain | Grey | White |
| Spinal Cord | White | Grey |
3. Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP)
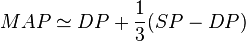
(From wikipedia)
4. Cryoprecipitate
A. Definition: FFP is thawed at 4°C, a precipitate remains, which can be separated by centrifugation --> cryoprecipitate (cryo)
B. 1U = 200 mg fibrinogen and 100 U Factor VIII
a. Content: vWF, factors VIII, XIII, fibrinogen, fibrinonectin
C. Indications:
a. Congenital and acquired deficiencies of fibrinogen and Factor XIII
b. vWD
D. Dose:
a. Bleeding in vWD: 1 unit/10 kg Q6-12 hr
b. Factor XIII deficiency: 1 unit/10 kg ONCE
E. Side effects: same as that of FFP
5. Free frozen plasma (FFP)
A. Hemostasis: activity of coagulation factors 35-30% of normal
a. Adult plasma volume: 40ml/kg, thus 10ml~15ml/kg --> 3~5U FFP
B. Content: coagulation factors and fibrinogen, fibrinonectin, vWF, etc.
B: Indications:
a. Bleeding from multiple factor deficiencies
a) Warfarin overdose
b) Vitamin K deficiency
c) Liver failure
d) Dilutional coagulopathy following massive transfusion
e) Reversing warfarin in preparation for an invasive procedure
b. Factor XI deficiency
c. INR>1.6
C. Dose: IV 10 to 15 mL/kg of BW
D. Healthy individual – 2 to 3 mL/kg/hour
a. Heart Failure - 1 mL/kg/hour
b. Pt on plasma exchange - 60 ~100 mL/minute
D. Side effects: Fever, allergic rxn, volume overload, Transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI)
6. Sperm Count
A. Number: 15,000,000/cc
B. Motility: 40%
7. Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) Criteria:
A. Temperature<36 °C (96.8 °F) or >38 °C (100.4 °F)
B. HR >90/min
C. RR>20/min or PaCO2<32 mmHg (4.3 kPa)
D. WBC<4x109/L (<4000/mm³), >12x109/L (>12,000/mm³), or 10% bands
E. Any 2 or more meets criteria!
*Sepsis = SIRS + Infection
*Severe sepsis = Sepsis + Organ Dysfunction/Hypotension/Hypoperfusion
1. Lactic Acidosis/SBP <90/SBP Drop ≥ 40 mm Hg of normal
*Septic shock = Severe sepsis + Hypotension (despite adequate fluid resuscitation)
*Multi-Organ failure: ≥ 2 Organs Failing
8. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS):
A. S/S: dyspnea, tachypnea, tachycardia, diaphoresis, cyanosis, chest pain, and use of accessory muscles of respiration. PE: diffuse crackles
a. 6 to 72 hours of an inciting event and worsen rapidly
B. Diagnosis:
a. Respiratory symptoms begun < 1 wk of a known clinical insult/new or worsening symptoms during the past wk.
b. CXR/CT: pulmonary edema, but not fully explained by pleural effusions, lobar collapse, lung collapse, or pulmonary nodules.
c. Respiratory failure not totally explained by HF/fluid overload
d. Impairment of oxygenation
*ABG --> PaO2 (mmHg), FiO2 (0.21 ~ 1)
*Alternative: SpO2/FiO2
a) Mild ARDS – The PaO2/FiO2 is >200 mmHg, but ≤300 mmHg, PEEP/CPAP ≥5 cm H2O
b) Moderate ARDS – The PaO2/FiO2 is >100 mmHg, but ≤200 mmHg, PEEP ≥5 cm H2O.
c) Severe ARDS – The PaO2/FiO2 is ≤100 mmHg, PEEP ≥5 cm H2O
C. Complications:
a. Barotrauma
b. Delirium
c. Nosocomial infection
d. DVT
e. GI bleeding from stress ulcers
f. Poor nutrition
g. Catheter-related infections
9. AKI vs. CKD
AKI
A. Diagnosis: AKIN Criteria:
a. ↑ serum CRE of 0.3 mg/dL/ >50% developing over <48 hours
a) Stage 1: ↑ CRE of 0.3 mg/dL or >50%
b) Stage 2: ↑ CRE of >100%
c) Stage 3: ↑ CRE of >200%
B. Diagnosis: Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO)-AKI) Criteria:
a. ↑ CRE of 0.3 mg/dL developing over 48 hours/ >50% developing > 7 days
a) Stage 1: ↑ CRE of 0.3 mg/dL or >50%
b) Stage 2: ↑ CRE of >100%
c) Stage 3: ↑ CRE of >200%
CKD
A. Definition:
a. GFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2
b. Kidney damage
c. >3 months
B. Revised CKD classification for based on GFR and albuminuria:
GFR
a. G1 - GFR >90 mL/min per 1.73 m2
b. G2 - GFR 60 to 89 mL/min per 1.73 m2
c. G3a - GFR 45 to 59 mL/min per 1.73 m2
d. G3b - GFR 30 to 44 mL/min per 1.73 m2
e. G4 - GFR 15 to 29 mL/min per 1.73 m2
f. G5 - GFR <15 mL/min per 1.73 m2/treatment by dialysis
Albumin excretion rate (AER)
a. A1 - <30 Normal -mildly ↑ (may be subdivided for risk prediction)
b. A2 - 30 to 300 Moderately ↑
c. A3 - >300 Severely ↑ --> then Nephrotic/non-nephrotic
10. Femoral triangle: NAVY
A. Lateral --> medial: Nerve --> Artery --> Vein --> Y of the groin
11. Virchow's Triad
A. Hypercoagulopathy
B. Hemodynamic changes
C. Endothelial injury
12. Late sign of IICP: Cushing's Triad
A. Cushing reflex : poor perfusion --> brain ischemia --> hypothalamus --> ↑PVR --> ↑BP --> parasympathetics by carotid-body baroreceptors --> vagal-induced bradycardia
B. Triad:
a. Widening pulse pressures
b. Hypertension
c. Irregular respirations (ex. Chyne-Stokes)
C. Tx:
a. Mannitol
b. Hyperventilation
c. Elevation of the head of bed
13. TORCH
T. Toxoplasmosis
O. Other viruses
R. Rubella
C. CMV
H. Herpes Simplex Viruses
14. VACTERL (VATER syndrome)
V. Vertebral anomalies
A. Anal atresia
C. Cardiac defects
TE. TE fistula/Esophageal atresia
R. Renal anomalies
L. Limb defects
15. DiGeorge Syndrome (CATCH 22)
C. Cardiac
A. Anbromal facies
T. Thymic hypoplasia
C. Cleft palate
H. Hypocalcemia
16. Down Syndrome

(From Wikispaces)
A. Cardiac problems
a. Endocardial cushion defect (ECD) ~40%
b. VSD ~35%
(Source: Uptodate)
沒有留言:
張貼留言